Union Auto Generate Primary Key View Sql Server
- Composite Primary Key Sql Server
- Union Auto Generate Primary Key View Sql Server Tutorial By Venkat
- Union Auto Generate Primary Key View Sql Server Download
- Pengertian Primary Key
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL primary key constraint to create the primary key for a table.
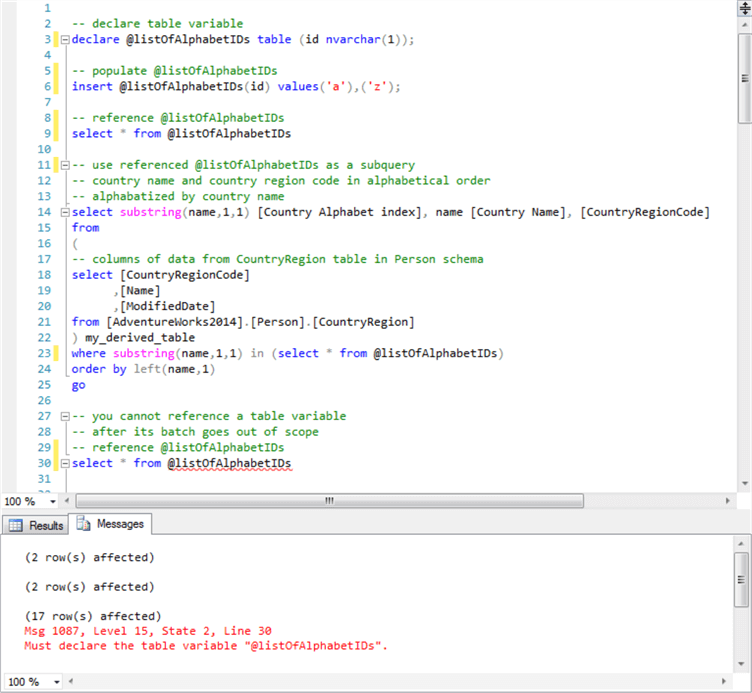
Jan 28, 2013 SQL Server - Primary key and Auto Increment of Primary Keys. SQL Server - Primary key and Auto Increment of Primary Keys. Skip navigation. Auto Generate. When you define a primary key for a table, MySQL automatically creates an index called PRIMARY. MySQL PRIMARY KEY examples. The PRIMARY KEY constraint allows you to define a primary key of a table when you create or alter table. 1) Define a PRIMARY KEY constraint in CREATE TABLE. Typically, you define the primary key for a table in the CREATE. Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQL Server PRIMARY KEY constraint to create a primary key for a table. Introduction to SQL Server PRIMARY KEY constraint. A primary key is a column or a group of columns that uniquely identifies each row in a table. You create a primary key for a table by using the PRIMARY KEY constraint. Primary Keys of Views¶ The primary key of a view is a column or a set of columns whose value is unique in this view. In Virtual DataPort, you can define the primary key of views. At runtime, clients can obtain the primary key definition of a view by invoking the appropriate methods of the JDBC and ODBC interfaces of the Server. Aug 17, 2006 Hi All, I have created a table using VIEWS in SQL server 2005, now i want to be ablle to edit it in a datagrid but i cannot do so as i there is no primary key! Now does anybody know how to set a.
You cannot create a primary key on a view. In SQL Server you can create an index on a view but that is different to creating a primary key. If you give us more information as to why you want a key on your view, perhaps we can help with that.
Introduction to MySQL primary key
A primary key is a column or a set of columns that uniquely identifies each row in the table. The primary key follows these rules:
This is a solution is specifically for users using Windows to SSH into their remote machines, including cloud images on Amazon AWS and GCE. This is useful when the SSH key is stored on a smart card (and access to the private key file is not possible). Generating a public key from a private key finder.
- A primary key must contain unique values. If the primary key consists of multiple columns, the combination of values in these columns must be unique.
- A primary key column cannot have
NULLvalues. Any attempt to insert or updateNULLto primary key columns will result in an error. Note that MySQL implicitly adds aNOT NULLconstraint to primary key columns. - A table can have one an only one primary key.
Because MySQL works faster with integers, the data type of the primary key column should be the integer e.g., INT, BIGINT. And you should ensure sure that value ranges of the integer type for the primary key are sufficient for storing all possible rows that the table may have.
A primary key column often has the AUTO_INCREMENT attribute that automatically generates a sequential integer whenever you insert a new row into the table.
When you define a primary key for a table, MySQL automatically creates an index called PRIMARY.
MySQL PRIMARY KEY examples
The PRIMARY KEY constraint allows you to define a primary key of a table when you create or alter table.
1) Define a PRIMARY KEY constraint in CREATE TABLE
Typically, you define the primary key for a table in the CREATE TABLE statement.
If the primary key has one column, you can use the PRIMARY KEY constraint as a column constraint:
When the primary key has more than one column, you must use the PRIMARY KEY constraint as a table constraint.
In this syntax, you separate columns in the column_list by commas (,).
The PRIMARY KEY table constraint can be used when the primary key has one column:
The following example creates a table named users whose primary key is the user_id column:
This statement creates the roles table that has the PRIMARY KEY constraint as the table constraint:
In case the primary key consists of multiple columns, you must specify them at the end of the CREATE TABLE statement. You put a comma-separated list of primary key columns inside parentheses followed the PRIMARY KEY keywords.
The following example creates the user_roles table whose primary key consists of two columns: user_id and role_id. It defines the PRIMARY KEY constraint as the table constraint:
Note that the statement also created two foreign key constraints.
2) Define PRIMARY KEY constraints using ALTER TABLE
If a table, for some reasons, does not have a primary key, you can use the ALTER TABLEstatement to add a primary key to the table as follows:
The following example adds the id column to the primary key.
First, create the pkdemos table without a primary key.
Second, add a primary key to the pkdemos table using the ALTER TABLE statement:
If you add a primary key to a table that already has data. The data in the column(s), which will be included in the primary key, must be unique and not NULL.
PRIMARY KEY vs. UNIQUE KEY vs. KEY
KEY is the synonym for INDEX. You use the KEY when you want to create an index for a column or a set of columns that is not the part of a primary key or unique key.
A UNIQUE index ensures that values in a column must be unique. Unlike the PRIMARY index, MySQL allows NULL values in the UNIQUE index. In addition, a table can have multiple UNIQUE indexes.
Suppose that email and username of users in the users table must be unique. To enforce thes rules, you can define UNIQUE indexes for the email and username columns as the following statement:
Add a UNIQUE index for the username column:
Add a UNIQUE index for the email column:
In this tutorial, you have learned how to create a primary key for a new table or add a primary key to an existing table.
- Was this tutorial helpful?
AUTO INCREMENT Field
Auto-increment allows a unique number to be generated automatically when a new record is inserted into a table.
Often this is the primary key field that we would like to be created automatically every time a new record is inserted.
Syntax for MySQL
The following SQL statement defines the 'Personid' column to be an auto-increment primary key field in the 'Persons' table:
Personid int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
PRIMARY KEY (Personid)
);
MySQL uses the AUTO_INCREMENT keyword to perform an auto-increment feature.
By default, the starting value for AUTO_INCREMENT is 1, and it will increment by 1 for each new record.
To let the AUTO_INCREMENT sequence start with another value, use the following SQL statement:
To insert a new record into the 'Persons' table, we will NOT have to specify a value for the 'Personid' column (a unique value will be added automatically):
VALUES ('Lars','Monsen');
The SQL statement above would insert a new record into the 'Persons' table. The 'Personid' column would be assigned a unique value. The 'FirstName' column would be set to 'Lars' and the 'LastName' column would be set to 'Monsen'.
Syntax for SQL Server
The following SQL statement defines the 'Personid' column to be an auto-increment primary key field in the 'Persons' table:
Personid int IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int
);
The MS SQL Server uses the IDENTITY keyword to perform an auto-increment feature.
In the example above, the starting value for IDENTITY is 1, and it will increment by 1 for each new record.
Tip: To specify that the 'Personid' column should start at value 10 and increment by 5, change it to IDENTITY(10,5).
To insert a new record into the 'Persons' table, we will NOT have to specify a value for the 'Personid' column (a unique value will be added automatically):
VALUES ('Lars','Monsen');
The SQL statement above would insert a new record into the 'Persons' table. The 'Personid' column would be assigned a unique value. The 'FirstName' column would be set to 'Lars' and the 'LastName' column would be set to 'Monsen'.
Syntax for Access
The following SQL statement defines the 'Personid' column to be an auto-increment primary key field in the 'Persons' table:
Personid AUTOINCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int
);
Composite Primary Key Sql Server
The MS Access uses the AUTOINCREMENT keyword to perform an auto-increment feature.
By default, the starting value for AUTOINCREMENT is 1, and it will increment by 1 for each new record.
Tip: To specify that the 'Personid' column should start at value 10 and increment by 5, change the autoincrement to AUTOINCREMENT(10,5).
To insert a new record into the 'Persons' table, we will NOT have to specify a value for the 'Personid' column (a unique value will be added automatically):
VALUES ('Lars','Monsen');
Union Auto Generate Primary Key View Sql Server Tutorial By Venkat
The SQL statement above would insert a new record into the 'Persons' table. The 'Personid' column would be assigned a unique value. The 'FirstName' column would be set to 'Lars' and the 'LastName' column would be set to 'Monsen'.
Union Auto Generate Primary Key View Sql Server Download
Syntax for Oracle
In Oracle the code is a little bit more tricky.
You will have to create an auto-increment field with the sequence object (this object generates a number sequence).
Use the following CREATE SEQUENCE syntax:
MINVALUE 1
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
CACHE 10;
The code above creates a sequence object called seq_person, that starts with 1 and will increment by 1. It will also cache up to 10 values for performance. The cache option specifies how many sequence values will be stored in memory for faster access.
To insert a new record into the 'Persons' table, we will have to use the nextval function (this function retrieves the next value from seq_person sequence):
VALUES (seq_person.nextval,'Lars','Monsen');
The SQL statement above would insert a new record into the 'Persons' table. The 'Personid' column would be assigned the next number from the seq_person sequence. The 'FirstName' column would be set to 'Lars' and the 'LastName' column would be set to 'Monsen'.
Advanced warfare release date. It all happens in year 2054.Always read your chosen stores product description before buying your Call Of Duty Advanced Warfare CD Key. Or can we handle more of the same with some fresh new skins?All we know right now is that the game is finally going to use a new engine. What gamers are really after is something 'fresh' from the franchise. It seems that they are actively listening, even if they won't respond directly. Check they are in stock, as well as any activation methods the cd key may require.