How Asymetric Public Private Key Pairs Are Generated
Dec 30, 2016 Symmetric encryption (private-key encryption or secret-key encryption) utilize the same key for encryption and decryption. Asymmetric encryption utilizes a pair of keys like public and private key for better security where a message sender encrypts the message with the public key and the receiver decrypts it with his/her private key. When an ICA client session is initiated, a unique public/private key pair is generated and passed through the communications channel. Once communication is established, these key pairs are used to arrive at the same RC5 symmetric key. Using a 1024-bit symmetric key, the client then begins processing ICA traffic and log-on information. Public key algorithms use two different keys: a public key and a private key. The private key member of the pair must be kept private and secure. The public key, however, can be distributed to anyone who requests it. The public key of a key pair is often distributed by means of a digital certificate. When one key of a key pair is used to encrypt a message, the other key from that pair is required to decrypt the.
- How Asymmetric Public Private Key Pairs Are Generated In Texas
- How Asymmetric Public Private Key Pairs Are Generated Mean
In asymmetric cryptography, the public and private key can also be used to create a digital signature. A digital signature assures that the person sending the message is who they claim to be. Typically, we use the recipient’s public key to encrypt the data and the recipient then uses their private key to decrypt the data. Mar 03, 2020 This page explains how to generate public/private key pairs using OpenSSL command-line tools. Device authentication. Cloud IoT Core uses public key (or asymmetric) authentication: The device uses a private key to sign a JSON Web Token (JWT). The token is passed to Cloud IoT Core as proof of the device's identity. Look around opensslpkeynew, or use the command line openssl tool to generate a key pair. – mario Aug 18 '14 at 20:57.
-->Creating and managing keys is an important part of the cryptographic process. Symmetric algorithms require the creation of a key and an initialization vector (IV). The key must be kept secret from anyone who should not decrypt your data. The IV does not have to be secret, but should be changed for each session. Asymmetric algorithms require the creation of a public key and a private key. The public key can be made public to anyone, while the private key must known only by the party who will decrypt the data encrypted with the public key. This section describes how to generate and manage keys for both symmetric and asymmetric algorithms.
Regcure pro licence key generator. Regcure pro license key generator in Title/Summary. RegCure Pro is a system maintenance tool that scans your registry, and other areas of Windows, for errors that are usually the cause of problems such as slowness, instability and system crashes. The program lists all the detected problems and allows you to fix them all in one go.
Symmetric Keys
The symmetric encryption classes supplied by the .NET Framework require a key and a new initialization vector (IV) to encrypt and decrypt data. Whenever you create a new instance of one of the managed symmetric cryptographic classes using the parameterless constructor, a new key and IV are automatically created. Anyone that you allow to decrypt your data must possess the same key and IV and use the same algorithm. Generally, a new key and IV should be created for every session, and neither the key nor IV should be stored for use in a later session.
To communicate a symmetric key and IV to a remote party, you would usually encrypt the symmetric key by using asymmetric encryption. Sending the key across an insecure network without encrypting it is unsafe, because anyone who intercepts the key and IV can then decrypt your data. For more information about exchanging data by using encryption, see Creating a Cryptographic Scheme.
The following example shows the creation of a new instance of the TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider class that implements the TripleDES algorithm.
When the previous code is executed, a new key and IV are generated and placed in the Key and IV properties, respectively.
Sometimes you might need to generate multiple keys. In this situation, you can create a new instance of a class that implements a symmetric algorithm and then create a new key and IV by calling the GenerateKey and GenerateIV methods. The following code example illustrates how to create new keys and IVs after a new instance of the symmetric cryptographic class has been made.
When the previous code is executed, a key and IV are generated when the new instance of TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider is made. Another key and IV are created when the GenerateKey and GenerateIV methods are called.
Asymmetric Keys
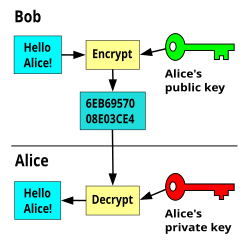
How Asymmetric Public Private Key Pairs Are Generated In Texas
The .NET Framework provides the RSACryptoServiceProvider and DSACryptoServiceProvider classes for asymmetric encryption. These classes create a public/private key pair when you use the parameterless constructor to create a new instance. Asymmetric keys can be either stored for use in multiple sessions or generated for one session only. While the public key can be made generally available, the private key should be closely guarded.
A public/private key pair is generated whenever a new instance of an asymmetric algorithm class is created. After a new instance of the class is created, the key information can be extracted using one of two methods:
The ToXmlString method, which returns an XML representation of the key information.
The ExportParameters method, which returns an RSAParameters structure that holds the key information.
Both methods accept a Boolean value that indicates whether to return only the public key information or to return both the public-key and the private-key information. An RSACryptoServiceProvider class can be initialized to the value of an RSAParameters structure by using the ImportParameters method.
Asymmetric private keys should never be stored verbatim or in plain text on the local computer. If you need to store a private key, you should use a key container. For more on how to store a private key in a key container, see How to: Store Asymmetric Keys in a Key Container.
The following code example creates a new instance of the RSACryptoServiceProvider class, creating a public/private key pair, and saves the public key information to an RSAParameters structure.